Polymorphonuclear neutrophils and Immunity
Polymorphonuclear neutrophils,
–also called polys for short,
–are phagocytes that have no mitochondria and get their energy from stored glycogen.
–They are nondividing, short-lived (half-life of 6–8 hours, 1–4 day lifespan), and have a segmented nucleus.
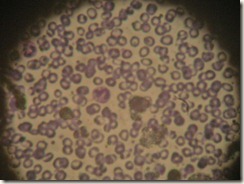
–[The picture below shows the neutrophil phagocytizing bacteria, in yellow.]
–They constitute 50–75% of all leukocytes.
–The neutrophils provide the major defense against pyogenic (pus-forming) bacteria and are the first on the scene to fight infection.
–They are followed by the wandering macrophages about three to four hours later